
Ten Tigers Martial Arts Las Vegas presents Guro Dino Flores and Guro Ariel Flores Mosses Seminar in Ilustrisimo & Lameco Eskrima. Las Vegas, Nevada, Saturday, April 29th, 2017 … [Read more...]
Mandirigma Research Organization

Ten Tigers Martial Arts Las Vegas presents Guro Dino Flores and Guro Ariel Flores Mosses Seminar in Ilustrisimo & Lameco Eskrima. Las Vegas, Nevada, Saturday, April 29th, 2017 … [Read more...]

Lameco Eskrima Practitioners Honor Punong Guro Edgar Sulite on his 20th Death Anniversary with training sessions and gatherings around the globe. Punong Guro Edgar Sulite September 25, 1957 – April 10, 1997 ------------ MADRID, SPAIN Madrid, Spain Group headed by Guro Tim Fredianelli: Honoring the memory of Punong Guro Edgar Sulite by training in Lameco Arnis in Madrid Spain. Our mode to all Lameco practitioners everywhere! Punong Guro Sulites 20th death anniversary. In Honor of Punong Guro Edgar Sulite we made a special training today. Our respects to our brothers from Lameco everywhere. -------- MEXICO CITY, MEXICO ------------- ZACATEPEC DE HIDALGO, MEXICO ------ PINTO, SPAIN Pinto Spain Group headed by Alfonso Lopez: On April 2 we did a training, in memory, and tribute to Punong Guro Edgar Sulite, in which we read the biography of Punong Guro, and performed a training with a great feeling, of course we had a memory of our brother recently deceased Alex Garduño, Our respects to all Lameco practitioners everywhere, Punong Guro Edgar Sulite 20th Death anniversary, and a special thanks to our Guros to keep alive the memory of Punong Guro. ----- LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA, USA ----- FOLSOM, NEW JERSEY, USA South Jersey Group headed by Jamie Morris … [Read more...]

How Filipino WWII Soldiers Were Written Out of History This post was written by Rosie Cima. You can follow her on Twitter here. Original Link: https://priceonomics.com/how-filipino-soldiers-were-written-out-of-the/ American and Filipino officers in the USAFFE in World War II (U.S. Army) From 1941-1944, hundreds of thousands of Filipino soldiers fought and died under the command of American generals against the Japanese in the Philippines. This struggle included one of the worst military defeats in U.S. history, and a grisly period of imprisonment and occupation. In exchange for their service in the United States Armed Forces of the Far East (USAFFE), Filipino soldiers were promised American citizenship and full veterans benefits. But Congress and President Truman reneged this offer in 1946. Only four thousand Filipino war veterans, out of an estimated 200,000 who survived the war, were able to get citizenship before the retraction was signed into law. You didn’t sleep through this section of US History. It was never taught. The role of Filipino soldiers in WWII has largely been erased from the history books. Building a Philippine Army In 1941, the United States suspected war with Japan was imminent. Whether they ‘knew’ Japan would strike Pearl Harbor is a matter of debate, but Japan had expanded its assaults to American allies. The Imperial Japanese objective was domination of all of Asia, and, having conquered Korea, parts of Russia, China and Taiwan, many of the countries that remained were colonial holdings of Western nations. According to an article in Salon: “[Roosevelt’s] administration had adopted the objective of defeating all the Axis powers and had begun the military and the economic planning to achieve it. He had shared that objective publicly with the American people, a large majority of whom now accepted war as inevitable.” The Philippines was a large American holding in the South Pacific. And what’s more, it was vulnerable. The Philippine army circa 1936 (Wikipedia) At the start of 1941, the Philippines had a meager army. It was a commonwealth of the United States from 1935 to 1946, and the US government was stewarding the archipelago's transition from a territory of the United States into an independent nation. Part of that transition should have involved amassing a Filipino military -- to replace the U.S. forces that had guarded the Philippines when it was a territory. But development of such a force was slow. Had the Japanese attacked the Philippines in January 1941, eleven months before Pearl Harbor, they would have encountered a few thousand American troops and a few thousand Filipinos. Which is why, in the summer of 1941, following the 1940 Japanese capture of French Indochina, the U.S. started recruiting a Philippine defense force like crazy. For the first few decades of the 20th century, because the U.S. “owned” the Philippines, Filipinos were considered U.S. “nationals.” U.S. nationals can work and reside in the U.S. without restriction, carry a U.S. passport, and apply for citizenship under the same rules as other resident foreigners. As a result, in 1940, there were about 45,000 Filipinos in the United States, most of them service-aged, male farm and factory laborers. Military service was then, as it is now, one of the shorter and more reliable paths for an alien to achieve citizenship. From 1941 to the end of the war, the government streamlined the hell out of that path. Filipino men were recruited into the U.S. military and given citizenship in mass naturalization ceremonies. Nearly one third of draft-age Filipinos in the continental U.S. volunteered for the Army. “When I reported to Los Angeles,” one Filipino-American WWII veteran is quoted in the book Filipino American Lives, “they swore me in as a U.S. citizen. I did not even have to file an application.” But the U.S. also recruited different branches of Philippine defenders from within the Philippines. Many of these individuals, and the Filipino immigrants who enlisted in the continental U.S., were motivated by a desire to protect the Philippines, their home, from an attack by the Imperial Japanese. Filipino soldiers in basic training (US Army) But the United States government sweetened the deal: President Roosevelt promised U.S. citizenship and full veterans benefits to Filipinos who took up arms against the Japanese. By late November, the United States Armed Forces in the Far East (USAFFE) was formed as the merger of the Philippine Commonwealth army and the US Armed Forces stationed in the Philippines. General Douglas MacArthur was made commander of the USAFFE. Ultimately, the allied forces in the Philippine campaign from 1941-1942 consisted of 120,000 Filipino troops and 30,000 American troops, some of whom were Filipino Americans. 8 Hours After Pearl Harbor The USS Arizona during the attack on Pearl Harbor (National Archives) When Pearl Harbor was … [Read more...]

February 28, 1997 By MO1
This article was reprinted with the author’s permission from the Souvenir Edition of Arnisador Magazine published by Goodwill Publications Limited. More information about the magazine can be obtained by calling Peter Morgan in London at +44 (0) 171-895 0800. Saturday, June 1st, 1996 LAMECO: Legacy of Steel By Steve Tarani Swollen knuckles, bleeding forearms and […]
April 10, 1997 By MO1
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.

January 10, 1998 By MO1
Kapisanang Mandirigma – A federation of warriors from different disciplines of the Warrior Arts of the Philippines. It is not a style, nor a representation of any singular style, but rather a federation of practitioners with similar goals to provide a vehicle for growth and personal discovery through continued training. Founded in 1998 by Guros […]
May 24, 1998 By MO1
Mandirigma.org - Online Since 1998 Mandirigma Research Organization also known as mandirigma.org is a project of Kapisanang Mandirigma. Their focus includes preserving and promoting the Warrior Arts commonly known as Kali, Eskrima and Arnis. The Warrior Arts is one of the most important aspects of any society because its very nature is to defend and preserve […]

February 21, 1999 By MO1
Baybayin Baybayin is a pre-Spanish Philippine writing system. It is a member of the Brahmic family and is recorded as being in use in the 16th century. It continued to be used during the Spanish colonization of the Philippines up until the late 19th Century. The term Baybay literally means “to spell” in Tagalog. Baybayin […]

May 18, 1999 By MO1
Kapisanang Mandirigma founders Guro Ariel Flores Mosses, Guro Arnold Noche, Guro Bud Balani and Guro Dino Flores mentioned in the Virtual Filipino Martial Arts Museum’s “Top 200 Living Guro’s” List Exerpt from: http://www.filipinomartialartsmuseum.com/index.htm Welcome to the Filipino Martial Arts Museum, the virtual museum and repository of knowledge of Filipino Martial Arts (FMA) systems, styles, […]

February 13, 2000 By MO1
Sticks of Death (Arnis: The Sticks of Death) This Filipino Martial Arts action film features Roland Dantes. Dantes plays Johnny Guerrero, a man who masters the ancient art of arnis with the help of his grandfather to get revenge on a group of crooks who attempted to beat him to death. Using two deadly sticks, […]

July 1, 2000 By MO1
The Battle of Manila – Starts with discussion from 2 Vets memories of the WW2 Japanese invasion and internment of civilians to the military incursion to rescue the civilian prisoners at Santo Tomas and Battle of Corregidor. Battle scenes in Philippines, views of rescued US civilians, street fighting in Manila at Intramuros, bridges destroyed. […]
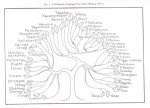
July 17, 2000 By MO1
“PHILIPPINE LANGUAGE TREE”, William Henry Scott (1984)

June 10, 2001 By MO1
June 12 as Independence Day by Diosdado Macapagal Former President of the Philippines “A nation is born into freedom on the day when such a people, moulded into a nation by a process of cultural evolution and sense of oneness born of common struggle and suffering, announces to the world that it asserts its natural […]

January 29, 2002 By MO1
The Moro Kris The kris is the most famous Moro weapon. Variations are found in every Moro tribe and it was a key symbol of a man’s status and rank in society as well as being a powerful talisman. Kris blades are wide at the base, double-edged, and can be waved, half-waved half-straight, or straight […]

January 26, 2003 By MO1
Inhabiting the rugged terrain of the Cordillera Region of Northern Philippines are six ethno-linguistic tribes known as the Ibaloy, Kankana-ey, Ifugao, Kalinga, Apayao/Isneg, and the Bontoc. They are referred to by a generic term, Igorot, a word coined from the root word, “golot” meaning mountain. Unlike most of the Philippines, which were ruled by Spaniards […]

May 23, 2003 By MO1
World Filipino Martial Arts Expo 2003, Bellevue, Washington
January 28, 2005 By MO1
The Butuan Silver Strip by Hector Santos © 1996 by Hector Santos All rights reserved. http://www.bibingka.com/dahon/mystery/silver.htm The Butuan area has been a rich source of material from ancient Philippines for both treasure hunters and trained archaeologists. So it was in the mid-seventies when a team from the National Museum of the Philippines excavating a site […]

May 23, 2006 By MO1
Noli Me Tangere is a novel by Filipino polymath José Rizal and first published in 1887 in Berlin, Germany. Early English translations used titles like An Eagle Flight and The Social Cancer, but more recent translations have been published using the original Latin title. Though originally written in Spanish, it is more commonly published […]

June 21, 2007 By MO1
Cordillera Administrative Region The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) of the Philippines is a land-locked region consists of the provinces of Abra, Benguet, Ifugao, Kalinga, Mountain Province and Apayao. Baguio City is the regional center. The Cordillera region encompasses most of the areas within the Cordillera Central mountain range of Luzon, the largest range in the […]

January 10, 2011 By MO1
Mandirigma Research Organization/Mandirigma.org, a project of Kapisanang Mandirigma, is a research organization dedicated to cultural research. Their focus includes preserving and promoting the Warrior Arts of the Philippines commonly known as Kali, Eskrima and Arnis. The Warrior Arts is one of the most important aspects of any society because its very nature is to defend […]
Copyright © 2026 · Lifestyle Theme on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in