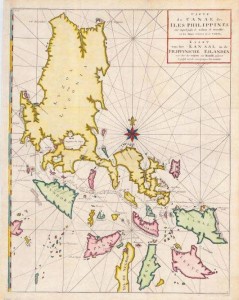
Guro Dino of the Mandirigma Research Organization met Professor Angel Postigo and his father on one of his many business trips to Los Angeles from Mexico. Professor Postigo is a person with a very impressive resume in the warrior arts and journalism, among other things, having written for Artes Marciales, Katana, Kung Fu Magazine, Legitima Defensa and National Sports Directory of Mexico. They found that they both have a passion for history and its relationship to the warrior arts. Some of the discussions they had concerned the connections between the Philippines and Mexico for hundreds of years. Professor Postigo felt that mandirigma.org would be an excellent venue to present his articles of this often overlooked relationship between the Philippines and Mexico in history. Quoting Professor Postigo, "The reason why I am interested in working with "mandirigma.org" is to showcase my work as a writer interested in disseminating and spreading the culture of the Martial Arts of the Philippines, work that I have done in several Mexican magazines." Friday, October 12th, 2007 The Two Conquests By Angel Postigo Suddenly, the ascent they had begun at the beach, finally ended. Thousands of miles behind, their guides had led them to cross between those two volcanoes, the Popocatepetl and the Iztacihuatl. Standing in the snow, those iron men and their heraldic horses had that spectacle at their feet: beyond this wooded spot of splendid beauty, far beyond, into those mountains, a wide green valley was extended, and in the center the lakes shined like silver, and above the islands and the banks, those citadels with plazas and wide roads, the high roofs of its temples upon splendid hand-painted pyramids, and the woods and great fields full of exotic plants that enlightened those magic days of autumn. For the first time, western men looked at that wonderful landscape, as if painted on the evening air, and their eyes glowed as they contemplated the plain and remembered the gold and sacred feathered presents they had been offered as a plead to retire, to stay away. Cortes and his soldiers had started the advance to that plain, to Tenochtitlan, and the battles were about to begin. The great lord of the empire, Moctezuma II, intelligent and educated man, though deeply superstitious as most of his people, knew that his kingdom had come to its end. The news had spread as a desperate scream: Quetzalcoatl has returned, the Serpent God that promised to return in the year one, Acatl (1519), the prophecies are fulfilled now, the white-skinned bearded God has returned. Moctezuma knows a battle against a God is impossible, he has to have the help of other gods in order to save his nation. Being Cortes an extremely skillful politician and warrior, he perceives the rivalries between the different towns, and above all, the exacerbated hate against the Mexicas and their Aztec empire. Cortes returned to Tenochtitlan, not before suffering a defeat known as the Sad Night, when fallen and surrounded he was spared as many soldiers thanks to the tradition of not killing the enemy, just defeating them to take some prisoners for the ritual sacrifices. According to the number of prisoners, those warriors, Eagle men and Jaguar men, ascended in their military ranges. They were true conquerors who went further their frontiers of Guatemala, but their conquest had seeded rancor against the Aztec empire. Their armies were the best armed and trained. They had a regular troop, Yaoquizquel, and a lower but considerable number of noble warriors, Pipiltin, who belonged to a society known as the Eagle men, Quauhtin, and Jaguar men, Ocelomeh. Their elegant clothing had the skins of those felines and the feathers of those sacred birds. They were the sons of nobles who went to the Calmecac to receive military and cultural education, they learned astronomy, rhetoric, poetry, but above all, religion, and their status was well established, and how they could ascent according to their bravery, but above all, to the number of prisoners caught in battle. The Tlamani were the ones in charged of guarding the prisoners. This noble warriors, elegantly dressed, had as their main weapons the Macuahuitl, a kind of long club with sharp obsidian points, a round shield made of leather named Chimalli, an arc known as Tlauitolli, and a throwing spear, Atlatl. As he walks through many different spots of this empire, Cortes realizes the situation. In some places he has battles, but in others he comes to agreements easily, accomplishing an alliance in the first year of his arrival, and after establishing the Villa Rica de la Vera Cruz. One of the alliances was with the Zapoteca people, and afterwards, with others oppressed by the Aztec empire, the Texcocanos, the Huejotzincas and the Totonacas. Cortes starts his first march towards Mexico, Tenochtitlan, on August 16th, 1519, towards the heart of the empire. He has only 400 Spanish soldiers, 15 horses, 3 canons, … [Read more...]