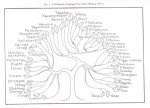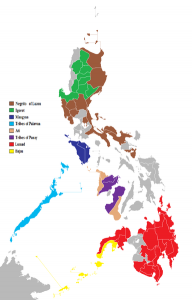
Indigenous peoples of the Philippines Indigenous peoples of the Philippines From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The indigenous peoples of the Philippines consist of a large number of indigenous ethnic groups living in the country. They are the descendants of the original inhabitants of the Philippines who have managed to resist centuries of Spanish and United States colonization and in the process have retained their customs and traditions.[1] In the 1990s, there were more than 100 highland tribal groups constituted approximately 3% of the population. The upland tribal groups were a blend in ethnic origin like other lowland Filipinos, although they did not have contact with the outside world. They displayed a variety of social organization, cultural expression and artistic skills. They showed a high degree of creativity, usually employed to embellish utilitarian objects, such as bowls, baskets, clothing, weapons and spoons. These groups ranged from various Igorot tribes, a group that includes the Bontoc, Ibaloi, Ifugao, Isneg, Kalinga and Kankana-ey, who built the Rice Terraces. They also covered a wide spectrum in terms of their integration and acculturation with lowland Christian and Muslim Filipinos. Native groups such as the Bukidnon in Mindanao, had intermarried with lowlanders for almost a century. Other groups such as the Kalinga in Luzon have remained isolated from lowland influence. There were several indigenous groups living in the Cordillera Central of Luzon in 1990. At one time it was employed by lowland Filipinos in a pejorative sense, but in recent years it came to be used with pride by native groups in the mountain region as a positive expression of their ethnic identity. The Ifugaos of Ifugao Province, the Bontocs, Kalinga, Tinguian, the Kankana-ey and Ibaloi were all farmers who constructed the rice terraces for many centuries. Other mountain peoples of Luzon are the Isnegs of northern Kalinga-Apayao Province, the Gaddangs of the border between Kalinga-Apayao, and Isabela provinces and the Ilongots of Nueva Vizcaya Province and Caraballo Mountains all developed hunting and gathering, farming cultivation and headhunting. Other indigenous people such as the Negritos formerly dominated the highlands throughout the islands for thousands of years, but have been reduced to a small population, living in widely scattered locations, primarily along the eastern ranges of the mountains. In the southern Philippines, upland and lowland tribal groups were concentrated on Mindanao and western Visayas, although there are several indigenous groups such as the Mangyan living in Mindoro. Among the most important groups found on Mindanao are collectively called the Lumad, and includes the Manobo, Bukidnon of Bukidnon Province, Bagobo, Mandaya, and Mansaka, who inhabited the mountains bordering the Davao Gulf; the Subanon of upland areas in the Zamboanga; the Mamanua in the Agusan-Surigao border region; the Bila-an, Tiruray and Tboli in the region of the Cotabato province, and the Samal and Bajau in the Sulu Archipelago. The tribal groups of the Philippines are known for their carved wooden figures, baskets, weaving, pottery and weapons. Reservation The Philippine government succeeded in establishing a number of protected reservations for tribal groups. Indigenous people were expected to speak their native language, dress in their traditional tribal clothing, live in houses constructed of natural materials using traditional architectural designs and celebrate their traditional ceremonies of propitiation of spirits believed to be inhabiting their environment. They are also encouraged to re-establish their traditional authority structure in which, as in indigenous society were governed by chieftains known as Rajah and Datu. Contact between “primitive” and “modern” ethnic groups usually resulted in weakening or destroying tribal culture without assimilating the indigenous groups into modern society. It seemed doubtful that the shift of the Philippine government policy from assimilation to cultural pluralism could reverse the process. Several Filipino tribes tends to lead to the abandonment of traditional culture because land security makes it easier for tribal members to adopt the economic process of the larger society and facilitates marriage with outsiders. In the past, the Philippine government bureaus could not preserve tribes as social museum exhibits, but with the aid of various nationwide organizations, they hoped to help the tribes adapt to modern society without completely losing their ethnic identity. … [Read more...]